How is Telecom Billing Done?
What is telecom billing and how it works
A telecom billing system manages all the data and processes a service provider needs to calculate and present invoices to their customers. Unique to telecom, the billing process also includes call rating and complex taxation.
Main steps in the telecom billing process
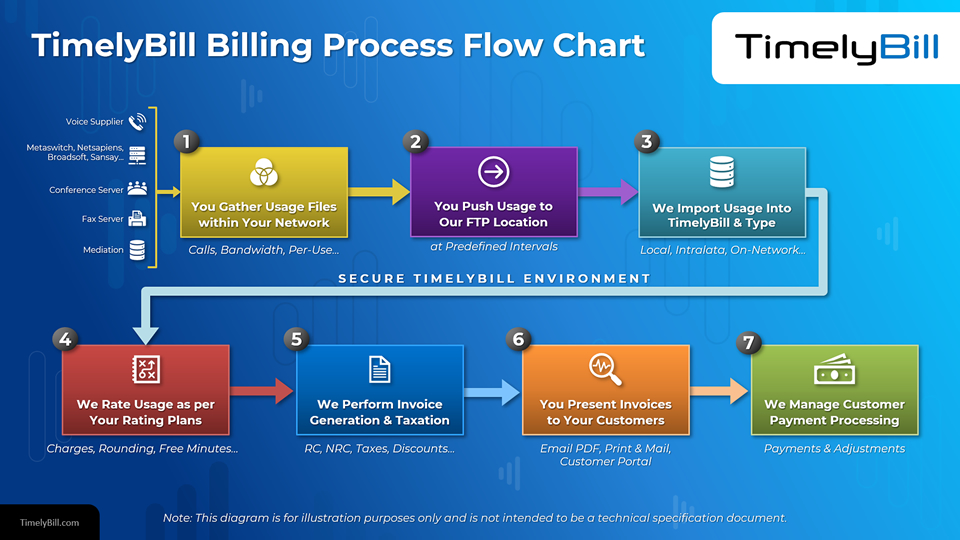
A telecom's billing cycle starts with gathering service usage files, typing the calls, applying charges, applying taxes and then generating the customer invoice. Billing also includes transmitting the invoices and recording customer payments and adjustments.
Usage gathering and call typing
Typical usage data includes message transactions, CDRs, bandwidth, per-use, etc. The billing process starts by you gathering your data files and pushing them to the billing system (typically via secure FTP). The billing system then establishes the type of "call". For example local, intralata, or on-network call types.
Call rating
This is where charges are calculated based on the pre-defined rate deck and applicable telecom taxes. The rating process takes each CDR and matches the originating phone number against the data to discover the customer and pricing to apply. Each call is then rated against the price level to calculate a cost.
CDR contents:
- Phone number dialed
- The originating phone number (used to identify the customer)
- Duration of call
- Date and time of the call
- Other fields (as needed)
Rate deck contents:
- Connection charges
- Minimum billable connection times
- Configurable call increments
- Call rounding options (up, down, round)
- Minimum and maximum calling charges
Billing and invoice generation
In this step, the billing system determines the fees, does the rounding of decimal places, and applies free minutes (if applicable). During invoice generation, the billing engine calculates a customer's recurring and non-recurring charges, taxes, discounts, etc.
Telecom invoice contents:
Every provider has a unique way of calculating rates, labeling services, and describing fees. A good invoice should help explain those determining factors. For better customer retention, service providers need to help their customers understand how their telecom invoices get calculated.
- Invoice formatting (profile and template)
- Contact information
- Custom messaging, with promotions, announcements etc.
- Frequency of bills with specific dates
- Summary of telecom charges, services and fees
- Detailed descriptions of all charges, services and fees
- One-time charges, recurring charges, and taxes
- Detailed usage/call history, or summary reports
- A "how to read this bill" section
Invoice transmission
Here, the billing software presents an invoice to your customer via email, print, or PDF format. Searchable and downloadable invoice data can be made available via an online customer portal.
Payment processing
This is where a billing system manages customer payment processing.
- Cash related payments
- Automated payments
- Real-time credit card payments
- ACH payments
- Lock box transactions
- Adjustments or refunds
Note, these steps describe the billing process for a typical communications service provider. TimelyBill's architecture is incredibly flexible and handle custom billing workflows to suit the needs of any modern telecom company.
Unfamiliar with a term in this process? Read our telecom billing glossary.
READ OUR BLOG POST:
TimelyBill Software Features
- Billing
- How Telecom Billing Works
- Usage Plans
- Usage Rater
- CDR Auditing & Margin Calculator
- Invoice Generator
- PDF Generator